1200V 10A Trench Field Stop IGBT TPGW10N120LN Topdiode (MAW10N120T1)
- High breakdown voltage to 1200V
- VCE(sat) = 1.85 V (typ.) @ IC = 10 A
- Very tight parameter distribution
- High ruggedness,temperaturestable behavior
- Short circuit withstand time – 10us
- High ruggedness, temperature stableLow VcE(SAT)
- Easy parallel switching capability due to positive temperature
- Coefficient in VcE(SAT)
- Enhanced avalanche capability
Topdiode 1200V 10A Trench Field Stop IGBT TPGW10N120LN (MAW10N120T1)
TOPDIODE TPGW10N120LN is an 1200V / 10A Trench Field Stop IGBT with TO-247-3 package.
TOPDIODE TPGW10N120LN has outstanding performance in Frequency Converters and Motor Drive.
Topdiode TPGW10N120LN is an alternative offer for Maximum IGBT MAW10N120T1.
Topdiode 1200V 10A Trench Field Stop IGBT TPGW10N120LN DATA
- Tab
| Topdiode PN | TPGW10N120LN |
| Description | IGBT |
| VCE | 1200V |
| IC | 10A |
| VCE(SAT) IC=15A | 1.85V |
| Package | TO-247-3 |
| Cross to Brand | Maximum |
| Pin to Pin Cross P/N | MAW10N120T1 |
Topdiode Hot Selling Products (6)
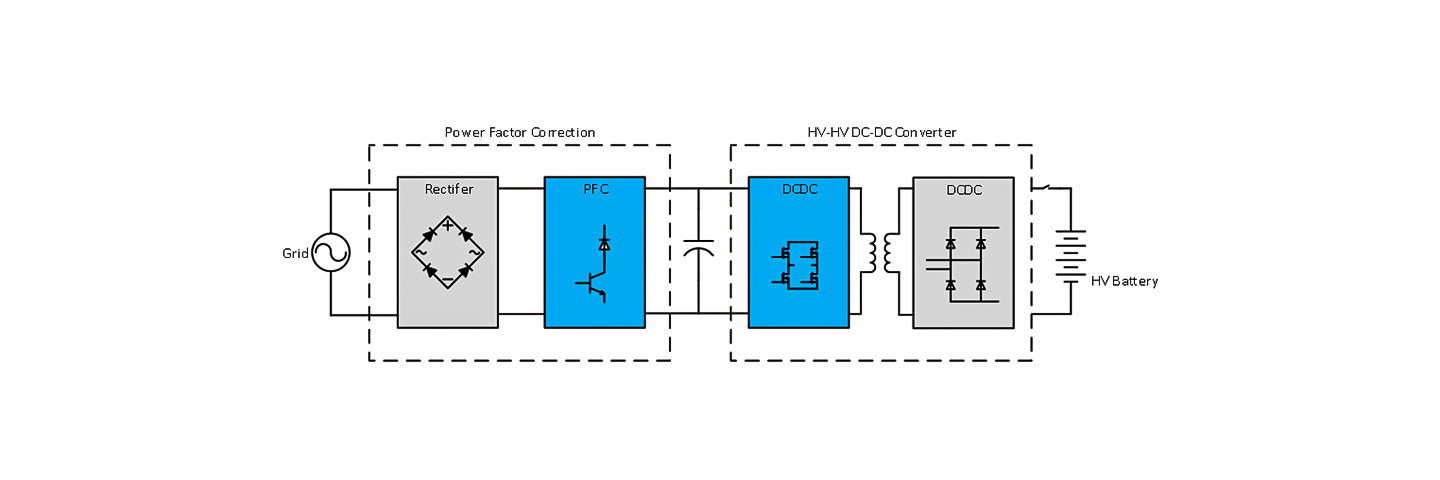
OBC Topdiode Mosfet, IGBT used on On-Board Charger (OBC)
An On-Board Charger (OBC) is a system built into a vehicle that is used to recharge the high-voltage battery from the AC grid when the vehicle is parked. At the heart of any electric (EV) or plug-in hybrid (HEV) vehicle lies the high-voltage (200 to 450VDC) battery and its associated charging system. Discrete high-voltage components are widely used in OBC (on-board charger) applications and, due to price pressure, are increasingly replacing module-based solution.
With a rich range of discrete semiconductor products, including Trench FSII technology IGBTs and Super-Junction Gen.3 TF series MOSFETs, we can provide cost-effective and energy-efficient solutions to achieve these challenging converter requirements.
Topdiode launched the Super Junction MOSFET III series. By optimizing the device structure design and adopting advanced manufacturing technology, product performance has been further improved, with better avalanche endurance and ESD capabilities, and improved reliability in device applications. At the same time, this series of products uses independent innovation technology to optimize the switching characteristics of the device, giving it better EMI performance in system applications and providing greater margin for system design.
PFC:
N-Channel Super Junction Power MOSFET TP65TF068T
N-Channel Super Junction Power MOSFET Ⅲ TP65TF041T
IGBT: 650V, 60A, Trench FS II Fast IGBT TP60TD65BT
650V, 60A, Trench FS II Fast IGBT TP60TD65BP
650V, 80A, Trench FS II TP80TD65BT TP80TD65BP
HV DC-DC:
N-Channel Super Junction Power MOSFET TP65TF099T\TP65TF041T

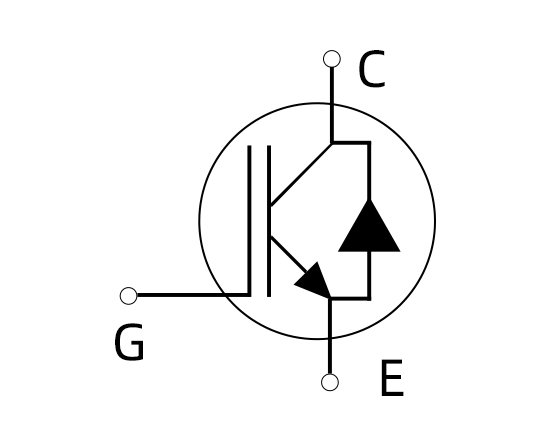
IGBT stands for insulated-gate bipolar transistor. It is a power transistor that combines an input MOS and an output bipolar transistor.
Here’s a brief explanation of how an IGBT works:
- Basics: An IGBT is made up of two main components – a P-type semiconductor and N-type semiconductor. These semiconductors are made of materials such as silicon, and they are joined together to form a p-n junction, which is the basic structure of a diode.
- Gate: The gate of an IGBT is an electrode that is used to control the flow of current between the p-type and n-type semiconductors. It is insulated from the rest of the device by a layer of Aluminum oxide or Silicon nitride, which prevents leakage current and ensures that the device operates only when the gate signal is applied.
- Bipolar: The term “bipolar” refers to the fact that the IGBT can conduct both positive and negative currents, unlike a uni-polar device such as a MOSFET, which can only conduct positive current. This allows the IGBT to handle higher power levels and operate more efficiently in certain applications.
- Operation: When the gate signal is applied, the IGBT is turned on, and current can flow between the p-type and n-type semiconductors. The amount of current that flows depends on the voltage applied to the gate and the resistance of the load connected to the IGBT. When the gate signal is removed, the IGBT is turned off, and no current can flow.
Some of the key features of IGBT include:
- High voltage and current handling capabilities: IGBTs can handle high voltage and current levels, making them suitable for use in high power applications. They can switch and control large amounts of power, making them an excellent choice for use in electric vehicles, solar inverters, and wind turbines, among other applications.
- Fast switching speed: IGBTs can switch on and off very quickly, which allows them to be used in high-speed applications such as power converters and motor controllers. Their fast switching speed also helps to reduce energy losses and improve overall system efficiency.
- Low conduction losses: IGBTs have low conduction losses, which makes them more energy-efficient than other types of power semiconductor devices. This feature is particularly important in applications where the device is required to conduct high currents for extended periods of time.
- High efficiency: IGBTs can achieve high efficiency levels in power conversion and control applications due to their low losses and fast switching speed. This feature is beneficial in applications where energy efficiency is a critical concern, such as in electric vehicles and solar inverters.
- Compact size: IGBTs have a smaller physical size compared to other types of power semiconductor devices, making them more suitable for use in compact and space-constrained applications. This feature is particularly important in applications such as aerospace, military, and transportation, where size and weight are critical factors.
Power electronics: IGBTs are commonly used in power electronics devices such as power supplies, motor controllers, and solar inverters.
Renewable energy: IGBTs are used in wind turbines and solar panels to convert DC power to AC power.
Traction applications: IGBTs are used in electric vehicles and trains to control the power flow and convert DC power to AC power.
Industrial automation: IGBTs are used in industrial automation equipment such as conveyor systems, robotics, and CNC machines.
Home appliances: IGBTs are used in various home appliances such as refrigerators, washing machines, and air conditioners.
Telecommunications: IGBTs are used in telecommunication equipment such as power amplifiers and base stations.
Medical equipment: IGBTs are used in medical equipment such as X-ray machines and surgical lasers.
Transportation: IGBTs are used in transportation systems such as elevators and escalators.
Defense and aerospace: IGBTs are used in defense and aerospace applications such as missile guidance systems and satellite power systems.
Alternative energy: IGBTs are used in alternative energy systems such as fuel cells and energy storage systems. IGBTs are versatile devices that are used in a wide range of applications due to their high efficiency, fast switching speeds, and low losses.
- High Voltage and Current Handling: IGBTs can handle high voltage levels and currents, making them suitable for power applications that require robust conduction capabilities.
- Fast Switching Speed: IGBTs have a fast switching characteristic, enabling efficient power regulation and modulation, and facilitating high-frequency operation.
- Low Saturation Voltage: IGBTs exhibit low voltage drop when conducting, resulting in minimal power losses and improved overall system efficiency.
- Easy to Control: IGBTs can be easily controlled by gate voltage, allowing for accurate and flexible power regulation.
- High Input Impedance: IGBTs possess a high input impedance, making them easily driven by low-power control signals and reducing the complexity of drive circuitry.
- Cost down. Reliable quality to replace Infineon, ST, AOS, TRINNO etc. Help our partners cost down.