Topdiode MBRS1100L K110L corss to Nexperia PMEG10010ELR
A Low Leakage Current Schottky Barrier Rectifier is a specialized diode that combines the fast switching and low forward voltage drop of standard Schottky diodes with significantly reduced reverse current, making it ideal for power-efficient electronics like portable devices, DC-DC converters, and SMPS, where minimizing wasted energy from leakage is crucial, often achieved using advanced materials (like SiC) or guard rings.
Key Characteristics
- Rectification:Like all diodes, it allows current to flow easily in one direction (forward) but blocks it in the other (reverse).
- Low Forward Voltage Drop(Vf): Lower power loss and less heat generation during conduction compared to standard P-N junction diodes.
- Low Leakage Current(Ir): The defining feature; it minimizes the unwanted reverse current that normally flows when the diode is blocking voltage, preventing battery drain and improving efficiency.
- Fast Switching:Retains the rapid switching speeds of Schottky diodes, crucial for high-frequency power applications.
How it Works (and Why it’s Special)
- Traditional Schottky Trade-off:Standard Schottky diodes achieve low Vf by using a low barrier height (ϕB), but this inherently increases leakage current (Ir).
- Low Leakage Solutions:
- Guard Rings:Integrated structures that protect the junction from electric field stress, preventing current leakage.
- Material Innovation:Using advanced semiconductors like Silicon Carbide (SiC) provides superior performance, allowing for high voltage, high temperature, and low leakage.
- High Barrier Height (MBR Type):Some designs use a higher barrier height metal (e.g., platinum or nickel) to reduce leakage at the cost of a slightly higher Vf, but with better temperature stability.
Applications
- Portable Electronics:Extends battery life by reducing standby power drain.
- High-Efficiency Power Supplies:For adaptors, servers, and DC-DC converters.
- Reverse Polarity Protection:Prevents damage from incorrect battery insertion.
- LED Backlighting:For efficient power management in displays.
Nexperia PMEG10010ELR 100 V, 1 A low leakage current Schottky barrier rectifier, Planar Schottky barrier rectifier with an integrated guard ring for stress protection, encapsulated in a SOD123W small and flat lead Surface-Mounted Device (SMD) plastic package.
Topdiode MBRS1100L / K110L can be replaced Nexperia PMEG10010ELR
MAXIMUM RATINGS AND ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS
Ratings at 25 C ambient temperature unless otherwise specified.
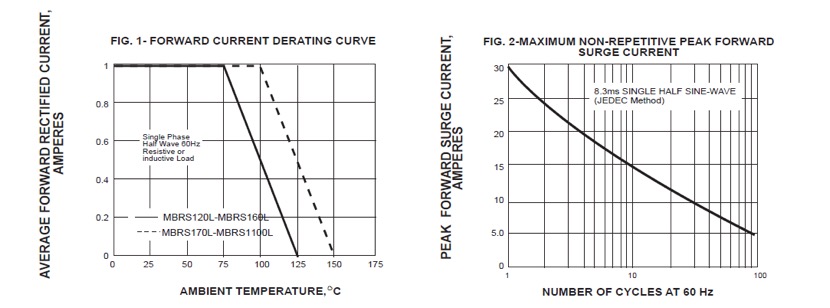
Single phase half-wave 60Hz,resistive or inductive load,for capacitive load current derate by 20%.
FEATURES
The plastic package carries Underwriters Laboratory
Flammability Classification 94V-0
Metal silicon junction,majority carrier conduction
Low power loss,high efficiency
High forward surge current capability
High temperature soldering guaranteed: 250 C/10 seconds,0.375”(9.5mm) lead length,
5 lbs. (2.3kg) tension
MECHANICAL DATA:
Case: JEDEC SOD-123FL molded plastic body
Terminals: Solderable per MIL-STD-750, Method 2026
Polarity: Color band denotes cathode end

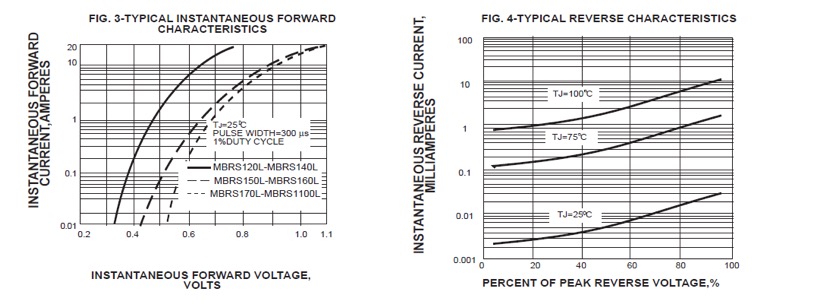
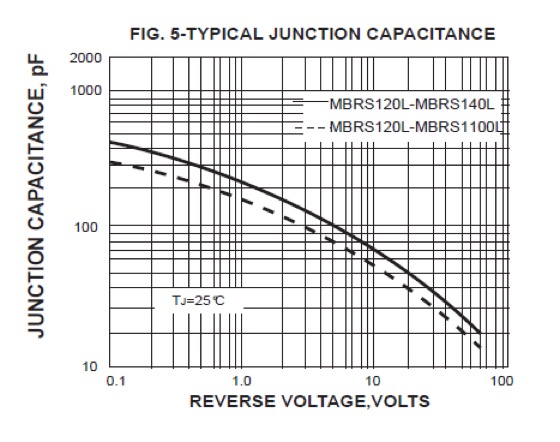
RATINGS AND CHARACTERISTIC CURVES MBRS120L THRU MBRS1100L
How does low leakage current Schottky barrier rectifier work:
Low leakage Schottky rectifiers work by creating a Metal-Semiconductor junction (Schottky barrier) that efficiently blocks reverse current through barrier engineering (like trenches or buried layers) to flatten electric fields, preventing current leakage often caused by surface defects in standard designs, allowing for faster switching and higher efficiency than PN junction diodes.
Standard Schottky Diode Operation
- Forward Bias: Electrons in the semiconductor gain enough energy to overcome the Schottky barrier (a potential hill) and flow into the metal, allowing current to pass easily with low voltage drop.
- Reverse Bias: The barrier height increases, blocking electron flow. However, normal Schottky diodes have surface irregularitiesor defects that concentrate the electric field, creating leakage paths.
How Low Leakage is Achieved (Engineering Techniques)
- Trench Schottky (Trench SBD): Grooves (trenches) are etched in the semiconductor and filled with polysilicon, acting as a field plate to spread out the electric field, reducing peak stress at the surface and thus lowering leakage.
- JBS (Junction Barrier Schottky): A p-type region is buried below the surface. As reverse voltage increases, the depletion regions from this buried layer and the surface meet, moving the peak electric field away from the surface defects and under the p-region, significantly reducing leakage.
- Material Choice & Interface Control: Using specific metals and carefully controlling the semiconductor surface (e.g., GaN with specific treatments) creates a higher, more uniform barrier and fewer interface states that cause leakage.
Why It Matters
These engineering techniques create a more robust reverse blocking capability, making the diode highly efficient for high-frequency applications, power supplies, and scenarios needing minimal power loss, despite the inherent tendency of Schottky diodes to leak more than PN diodes.
Topdiode provides the following low leakage current Schottky barrier rectifier MBRS120L THRU MBRS1100L



