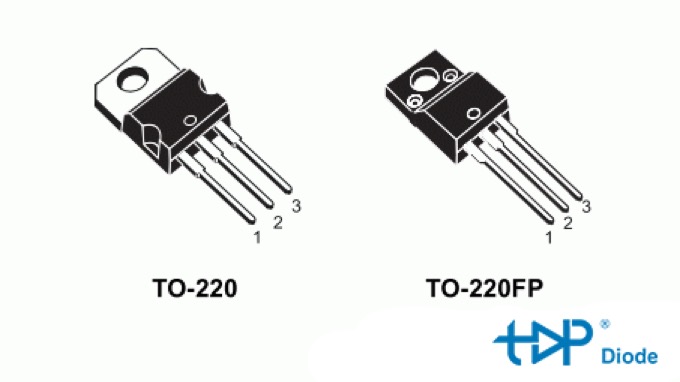
TO-220 Package Features, Variants, Advantages, and Limitations
Topdiode TO-220 is a widely used package type for various electronic components, including power transistors, voltage regulators, and fast recovery diodes. This through-hole package features a metal tab with a mounting hole, allowing secure attachment to a heatsink for efficient thermal dissipation. Its design makes it ideal for high-power applications where effective heat management is crucial.
Structure and Design
A standard TO-220 package typically consists of a metal tab and three leads, although versions with more leads are available to meet different application needs. The metal tab is usually connected to the center lead, enabling both thermal and electrical performance optimization in circuit design.
TO-220 Package Dimensions and Pinout
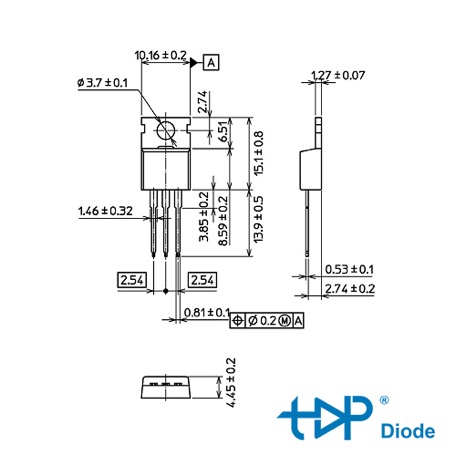
The TO-220 is a standard package for semiconductors and has specific physical dimensions. However, please note that dimensions might have slight variations based on manufacturers or specific versions of the TO220 package. The typical dimensions can be described as follows:
– Total length: Around 15 mm
– Total width: About 10 mm
– Thickness (excluding leads and heatsink tab): Roughly 4.5 mm
– Lead length: Around 14 mm
– Lead separation or pitch (centre to centre of lead at the point they emerge from the case): 2.54 mm (0.1 inches), matching the standard breadboard and perfboard pitch
– Diameter of hole in the heat tab: Roughly 3.2 mm
Pinout
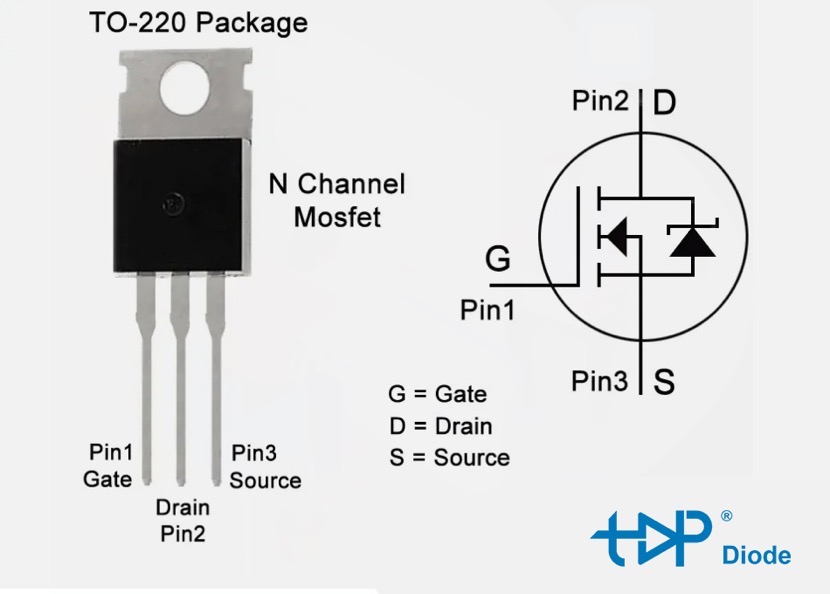
The TO-220’s heatsink tab is usually connected to the center pin (or to some part of the semiconductor die). When incorporating a TO-220 package component in a circuit, it’s crucial to account for these dimensions. This ensures adequate space is provided for both the component and any heatsink that it’s attached to. It also ensures that the device fits on the printed circuit board (PCB) and doesn’t interfere with neighbouring components.
Common Variants
The TO-220 family includes several variants, each designed to address specific application requirements:
Standard TO-220: The most common form, featuring a mounting tab and three leads for connection to a heatsink and PCB.
TO-220F (Fully Isolated): Comes with an insulated tab to prevent electrical contact with the heatsink, making it suitable for applications requiring electrical isolation.
TO-220AB: Similar to the standard version but with an extended metal tab for improved heat dissipation.
TO-220AC: Features a different lead bend compared to the standard TO-220.
TO-220D: Designed with horizontal orientation and side leads.
In addition to the three-lead configuration, TO-220 packages are also available with two, four, five, six, or even seven leads for expanded functionality.
Advantages of TO-220
Excellent Heat Dissipation – The large metal tab can be bolted directly to a heatsink, efficiently transferring heat away from the component and preventing thermal damage.
Versatility – Compatible with a wide range of components such as transistors, regulators, and diodes. Available in multiple lead configurations to suit various designs.
Durability – The robust design ensures reliability even under harsh operating conditions, contributing to longer component lifespan.
Ease of Assembly – Being a through-hole package, TO-220 devices are relatively easy to handle, solder, and replace, making them suitable for prototyping and low-volume production.
Model Variety – Multiple variants, including insulated versions like the TO-220F, provide greater flexibility for electrical and thermal design requirements.
Cost-Effectiveness – Offers a balance between performance and affordability, making it a practical choice for many applications.
Limitations of TO-220
While the TO-220 package offers many benefits, engineers should also consider its drawbacks:
Size and Space Requirements – TO-220 is larger than surface-mount counterparts, making it less suitable for compact consumer electronics where PCB real estate is limited.
Not Ideal for High-Frequency Circuits – Long leads can introduce parasitic inductance and resistance, potentially affecting performance in high-speed applications.
Additional Thermal Management Needs – High-power designs may still require extra thermal solutions like thermal paste or large heatsinks, adding cost and complexity.
Proper Mounting Required – For optimal heat dissipation, the package must be correctly mounted to a heatsink. Improper installation can lead to overheating and failure.
Live Metal Tab – In standard TO-220 packages, the tab is electrically active (often connected to the center lead), which may require additional insulation or use of an isolated version.
What is the difference between TO-220 and to 220F?
The primary difference between the TO-220 and TO-220F packages is related to the design and functionality of the metal tab that’s typically used for heat dissipation.
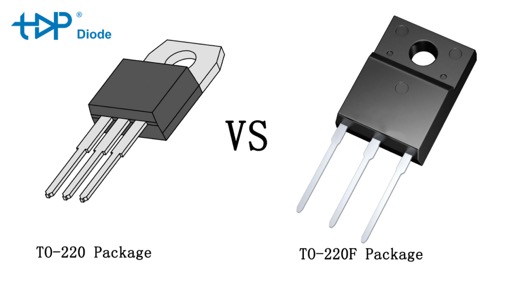
TO-220
In the standard TO-220 package, the metal tab is typically connected electrically to the middle lead (often the collector of a transistor or the drain of a FET), or some part of the semiconductor die. This means that when the component is mounted to a heatsink, an insulating layer is often necessary to prevent electrical short circuits, depending on the design of the system.
TO-220F (Full Pack) Package
The “F” in TO-220F stands for “Fullpack”, indicating that the package has a fully insulated tab. This means the tab is electrically neutral and not connected to any of the internal semiconductor structures. This design allows the TO-220F to be mounted directly to a heatsink without the need for additional insulation to prevent electrical shorts. This can simplify assembly, but it might come with a minor loss in thermal conductivity due to the insulating layer.
Both package types have the same basic form and pin configuration, so the choice between the two typically depends on the specific requirements of the system being designed. In a situation where electrical isolation is crucial, a TO-220F might be preferred, whereas a standard TO-220 might be perfectly suitable in other instances.
Applications
Thanks to its robust build, efficient heat management, and versatility, the TO-220 package is widely used in sectors ranging from audio equipment and automotive electronics to power supplies and industrial control systems.
In summary, the TO-220 remains a preferred choice for high-power, through-hole applications, offering a proven balance of performance, cost, and durability—provided that its size, high-frequency limitations, and thermal requirements are properly managed.