What are MOSFETs – Super-junction MOSFET
Features and Positioning of Power Transistors
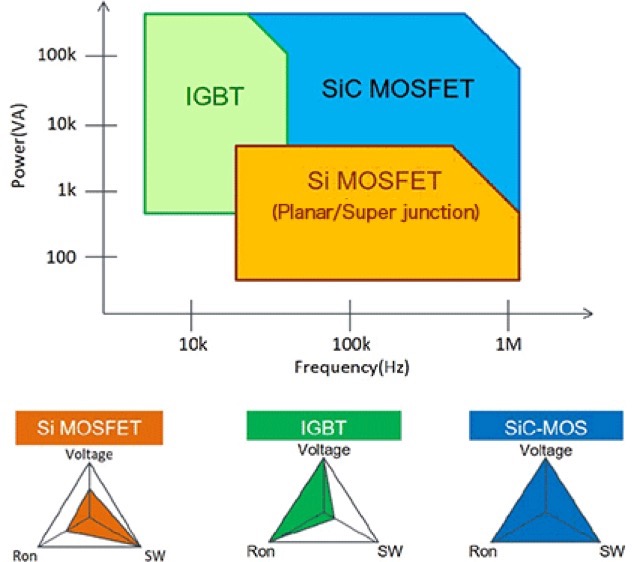
Let us begin by reviewing the power and frequency ranges covered by the principal power transistors of recent years, which are Si-MOSFETs, IGBTs, and SiC-MOSFETs. Hereafter we will be focusing on super-junction MOSFETs, but it will be useful to understand the position of Si-MOSFETs in the market in order to be able to understand how they are used selectively according to their features and characteristics.
The following graphic illustrates the power and frequency regions that can be handled by the different types of power transistors. We see that Si-MOSFETs lag behind IGBTs and SiC-MOSFETs somewhat with respect to ON-resistance and rated voltage, but are well-suited to high-speed operation at lower to intermediate power levels.
Planar MOSFET and Super-junction MOSFET
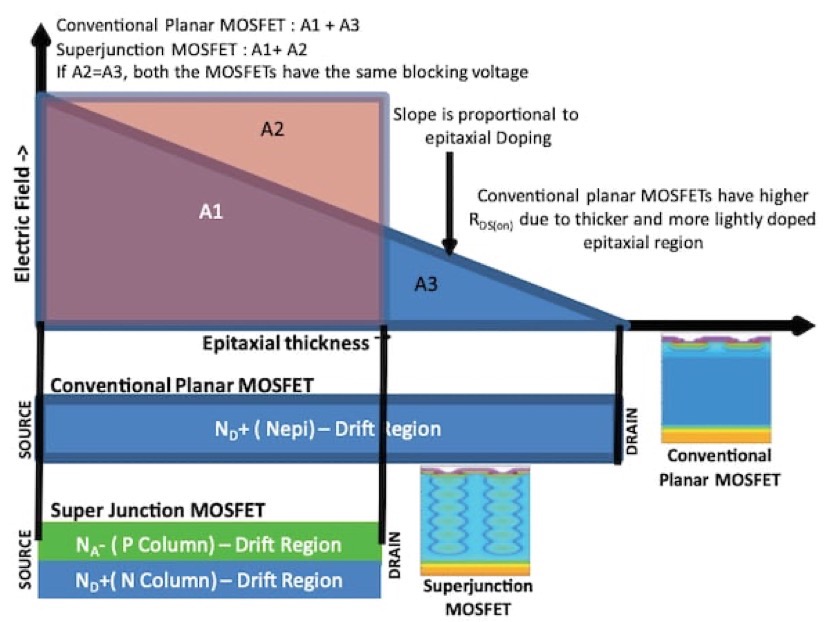
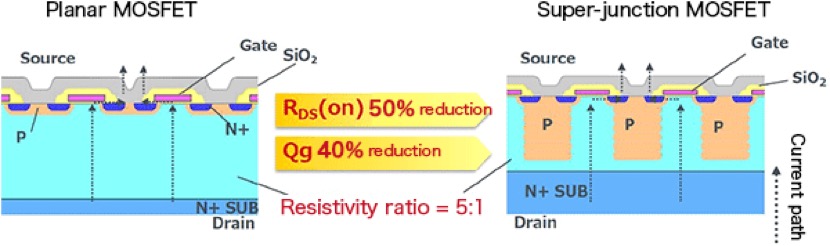
Si-MOSFETs can be classified as planar MOSFETs and super-junction MOSFETs according to the manufacturing processes used. Put simply, in the field of power transistors, the super-junction structure was developed in order to transcend the limits of planar structures.
As indicated in the graphic below, a planar structure constitutes a flat or planar transistor. This structure has had the drawback that if the rated voltage is raised, the drift layer becomes thicker, and so the ON-resistance is increased. In contrast, a super-junction structure is a structure in which multiple vertical pn junctions are arranged, as a result of which a low ON-resistance RDS(ON) and reduced gate charge Qg are realized while maintaining a high voltage.
In addition, the reverse current irr and the reverse recovery time trr of the internal diode are parameters that need to be studied for the turn-off switching characteristics of a transistor. As indicated in the waveform diagram below, in essence a super-junction MOSFET has a larger pn junction area than a planar MOSFET, and so trr is faster than for a planar MOSFET, but a larger irr flows.
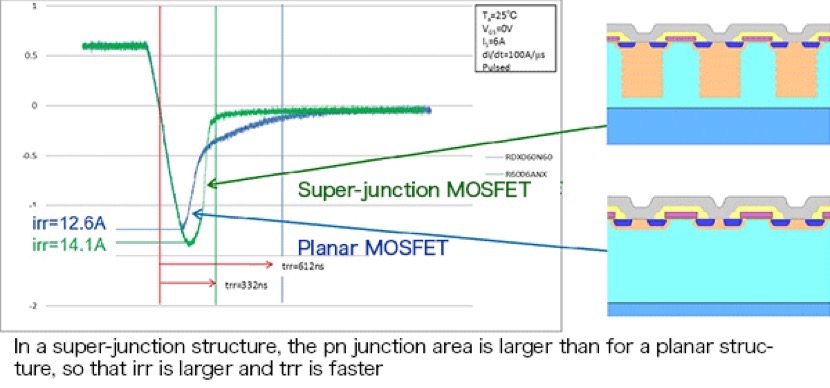
This characteristic, one issue with super-junction MOSFETs, is steadily undergoing improvement, and such features as fast operation and low noise endow super-junction MOSFETs with considerable variety. In the following sections, we will review features for a variety of MOSFETs.
IGBT
Topdiode IGBTs (Insulated Gate Bipolar Transistors) contribute to improved efficiency and energy savings in a variety of high voltage/current applications. Commonly used as switches in electronic devices, IGBTs are characterized by three terminals and metal oxide semiconductor gate structure.
Combining fast, smooth switching capabilities with high efficiency that saves energy while maintaining performance in everything from electric vehicles (EVs), trains, AC, and portable welding machines to AC-DC inverters and switching power supplies.
SiC MOSFETs
SiC MOSFETs eliminate tail current during switching, resulting in faster operation, reduced switching loss, and increased stabilization. Lower ON resistance and a compact chip size result in reduced capacitance and gate charge. In addition, SiC exhibits superior material properties, such as minimal ON-resistance increases, and enables greater package miniaturization and energy savings than silicon (Si) devices, in which the ON resistance can more than double with increased temperature.
Topdiode’s 4th Generation SiC MOSFET
Our latest 4th Gen SiC MOSFETs provide industry-leading low ON resistance with improving short-circuit withstand time. Additional features include low switching loss and support for 15V gate-source voltage that contributes to further device power savings.
MOSFETs
Topdiode MOSFETs feature low on-resistance and high switching speed. We offer a wide voltage lineup from small signal products to 800V high voltage products, and can be used for various applications such as power supplies and motor drive circuits.