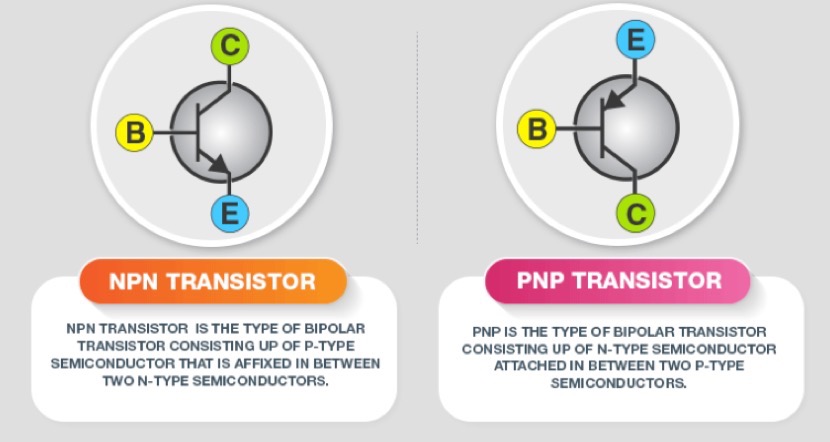
What are the differences between NPN and PNP transistors
Transistors: The Foundation of Modern Electronics
Transistors may be the most important invention in the field of electronic engineering and the foundation of almost all integrated circuits (ICs). A transistor is a three terminal electronic device that can be used to control the flow of current and was also the first electronic device capable of amplifying or switching current. This simple device can be used to create complex electronic circuits. Although there are other types of transistors, bipolar junction transistors are still widely used in digital circuits.

BJT Types and Basic Structure
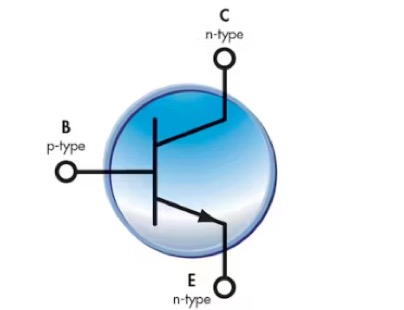
There are two main types of transistors: bipolar junction transistors (BJTs) and field-effect transistors (FETs). BJTs are made of doped materials and can be configured as NPN and PNP types. A transistor is an active device with three terminals called the emitter (E), base (B), and collector (C). The base is responsible for controlling the transistor, the collector is the positive electrode, and the emitter is the negative electrode
Four Key Operating Regions
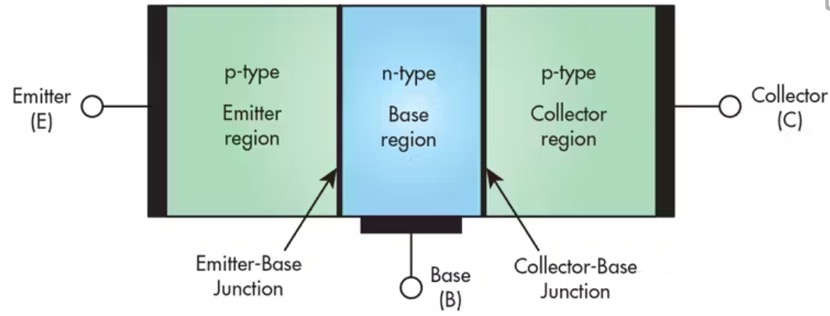
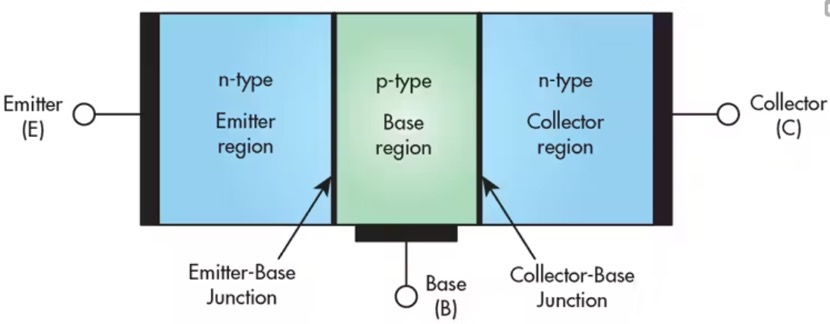
BJT consists of three independently doped regions, each with two junctions. PNP transistors have an N region between two P regions, while NPN transistors have a P region between two N regions, as shown in the following figure
- Cut off zone: BJT operates in this zone during switching operations. In the cut-off state, the transistor is in an inactive state.
- Activity area: BJTs operate in this area of the amplifier circuit, as transistors can act as fairly linear amplifiers.
- Saturation region: BJTs operate in this region during switching operations. The collector and emitter terminals of the transistor exhibit a nearly short circuited state.
- Reverse active region: Similar to active mode, the current is proportional to the base current, but flows in the opposite direction. This mode is rarely used.
Current Flow Direction: NPN vs. PNP
In NPN transistors, applying a positive voltage to the collector causes current to flow from the collector to the emitter. In PNP transistors, applying a positive voltage to the emitter causes current to flow from the emitter to the collector. In NPN transistors, current flows from the collector (C) to the emitter (E)
The basic principle of any BJT is to control the current of the third terminal by controlling the voltage between the other two terminals. The working principle of NPN and PNP is completely the same. The only difference lies in their bias method and the polarity of each type of power supply
Difference between NPN and PNP transistors
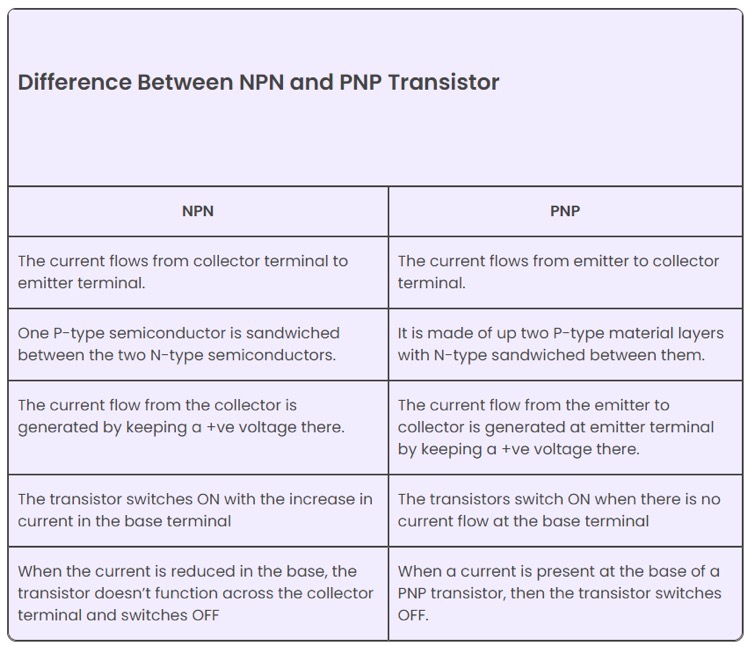
PNP transistors conduct through low signal, while NPN transistors conduct through high signal. In PNP transistors, P represents the polarity of the emitter and N represents the polarity of the base.
In NPN, N represents a coating with a negative charge on the material, while P represents a layer with a positive charge.
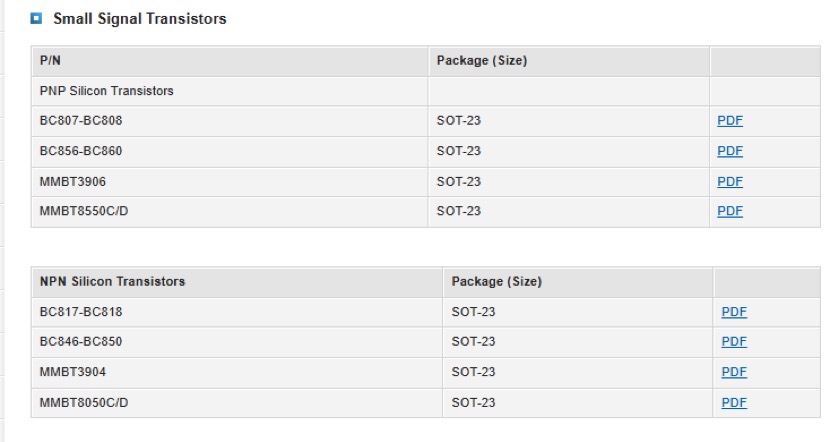
Product Spotlight: Small Signal Transistors
Topdiode is manufacturer for small signal transistors in China. Topdiode offer fast delivery for small signal transistors. Topdiode is very competitive supplier for small signal transistors BC807 BC808 PNP Silicon Epitaxial Planar Transistors, BC856 BC857 BC858 BC859 BC860 Small Signal Transistor, MMBT3906 PNP Silicon General Purpose Transistor, BC817 BC818 NPN Silicon Epitaxial Transistor, MMBTA14 NPN Silicon Epitaxial Planar Transistors, BC846DW~BC850DW, MMBT7002, 2N2907-2N2907A, MMBT458, TLT6354SL, BC8456DE-BC8458DB, MPSA42U, BC856W~BC860W.
For any questions or inquiries, please visit the website:https://www.topdiodes.com/



