Working principle of Zener diode
What is a Zener diode
Zener diode is a type of pn junction diode. When a reverse bias voltage is applied to a pn junction diode and this reverse voltage is increased, the current will sharply increase at a certain voltage (Zener voltage/breakdown voltage). Zener diode is a diode that utilizes this characteristic to generate a constant voltage.

Working principle of Zener diode
The role of a Zener diode in forward bias is similar to that of a regular diode. Then, once the reverse voltage equals its rated voltage, the current is allowed to flow in reverse.
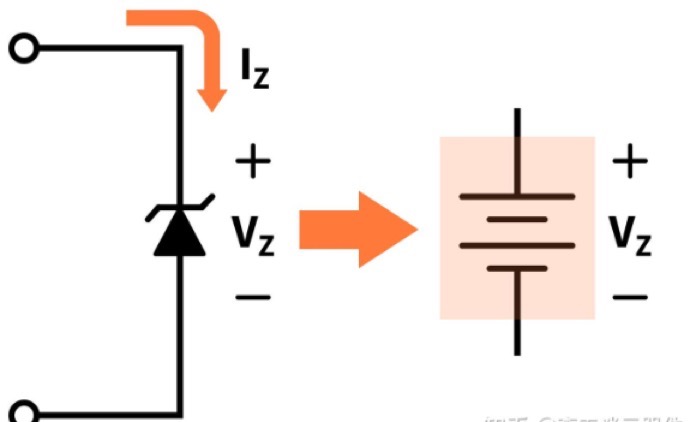
The breakdown working Zener diode acts as a voltage regulator because it maintains an almost constant voltage across its terminals within a specified range of reverse current values, which is equal to the Zener voltage. The constant voltage drop across the Zener diode caused by reverse breakdown is represented by the DC voltage symbol.
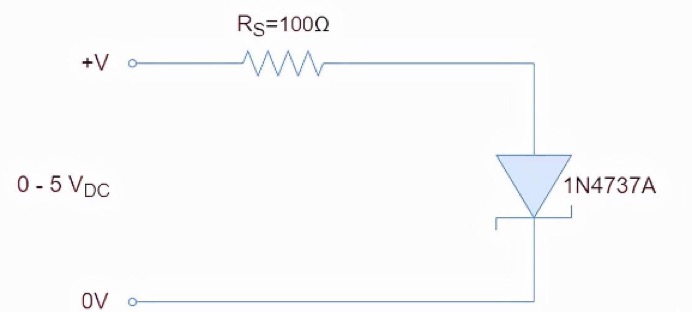
The Zener diode is forward biased
The forward characteristic of a Zener diode is similar to that of a simple diode, and the forward current is an exponential function of the forward voltage drop. A small change in voltage drop can cause a rapid increase in current. Usually, a voltage drop of 0.8 volts across the PN junction is sufficient to forward bias the Zener diode. The forward biased Zener diode is shown below:
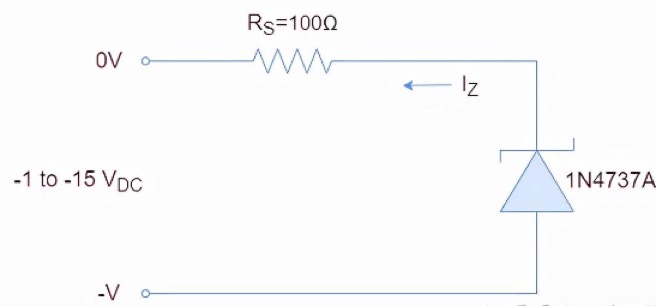
The Zener diode is reverse biased
When a regular diode operates in reverse bias mode, no current flows through it. In this case, a large amount of electron flow may damage the diode. However, in Zener diodes, Zener breakdown occurs due to the strong electric field generated by the thin depletion layer of the PN junction. The voltage at which Zener breakdown occurs is called VZ (Zener voltage).
According to application and voltage requirements, the produced Zener diodes have different levels of Zener voltage. Once Zener breakdown occurs, further increase in reverse voltage will not cause any further voltage drop and will remain constant at a certain voltage level until avalanche breakdown occurs.
In short, for a reverse biased Zener diode, it remains turned off (with a small amount of current flowing) from 0V to the Zener voltage (VZ). From VZ to avalanche breakdown, small changes in applied voltage can cause a rapid increase in reverse current. The reverse biased Zener diode is shown in the following figure
Zener diodes are used in various applications, including:
voltage control
voltage reference
surge suppression
Switch application
lipping circuit
Topdiode supplies zener diodes for voltage regulation circuits as bellow:
Topdiode has competitive prices and shorter lead times compared to other brands. Topdiode services are designed to meet the needs of customers seeking cost savings with faster project timelines.
We can offer the following rectifier bridge
For any questions or inquiries, please visit the website:https://www.topdiode.com/
BZX55C2V7~47V DO-35
BZV55C2V4~47V LL-34
1N4729A~1N4756A DO-41
ZM4728~ZM4761 LL-41
BZX84C3V0-47V



